High Resolution Melting technology is a new genetic analysis method for mutation scanning and genotyping that has emerged in recent years. HRM is not limited by the location and type of mutated bases. Without the need for sequence-specific probes, high-resolution melting can be run directly after PCR to complete the analysis of the sample. Compared with other genetic typing techniques, this method has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, low cost and high throughput detection, and is a rapid, inexpensive and effective method for detecting mutations.
HRM principle
HRM is a method for detecting mutations by measuring the change of DNA double-strand melting curve on the basis of PCR. The change of the dissolution curve depends on the DNA sequence, length, and GC content. Therefore, the change of the melting curve can be monitored by saturated fuel to reflect the properties of the nucleic acid. Differences to analyze the sample.
In the detection of the dissolution curve of the duplex, it is necessary to add a suitable dye, and a saturated dye such as SYBR Green may rearrange in the double-strand melting process, and the DNA melting cannot be truly reflected. Not suitable for samples that require low temperature melting and cannot detect heteroduplexes. Therefore, it cannot be used for the detection of the melting curve. LC Green is a saturated dye with a stronger binding site to DNA and has little inhibition on PCR. It has been successfully used in HRM detection.
HRM is easy to operate, adding appropriate dyes after the end of PCR, by monitoring the combination of fluorescent dyes and PCR amplification products during the heating process. During the heating process, the double strands are unfolded and the fluorescent dyes are separated from the melting molecules. The release is accompanied by a decrease in the fluorescence intensity, so that it is possible to judge whether or not there is a mutation by the change in the fluorescence intensity and the curve.
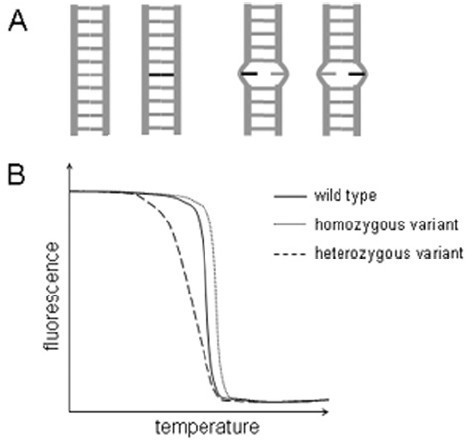
Figure 1: Melting curve of homoduplex and heteroduplex

Figure 2: HRM data processing
HRM features and applications
HRM application:
- Detection of autosomal recessiveness and X-linkage in human disease-associated genes
- Identification of somatic mutations in human tumors, screening for somatic mutations in tumor samples
- Gene mutation scan: single base change, insertion or deletion
- Specific mutations, screening of polymorphic sites
- Exon and short amplicon genotype scanning
HRM features:
- High sensitivity: The sensitivity of the detection of heterozygous mutants can reach 100%. In principle, the homozygous or hemizygous mutations are not detected after the temperature increase in the data analysis, but in fact, many homozygous mutations can be detected. of. If the gene mutation is exactly linked to x, a known wild-type sample can be added prior to PCR to detect a hemizygous or homozygous mutation.
- Good specificity: HRM specificity can reach 90-100%. Short amplicon specificity is higher
- Not limited by base sites, wide range of applications
- In a closed test tube, it can reduce pollution and easy operation.
- Low cost, low time, small error, high throughput detection
- Wide range of samples tested: HRM detection fragments ranging from 38 to 1000 bp samples from different sources can be used for HRM such as blood meal, oral cells, frozen tumor samples, alcohol fixation, formalin fixation or paraffin embedding Tissues, etc. In the study of human genetic diseases, DNA is usually extracted from peripheral blood lymphocytes for HRM analysis.
HRM: issues to consider in experimental design
- The design of an efficient amplification protocol is critical to the success of HRM. Maximum sensitivity and specificity contribute to optimal PCR results, while the solubility characteristics of the amplicon are also important for the results. This depends on the design of the primer and the position of the primer.
- False positives sometimes occur in experimental results, and false negative results can be avoided by adjusting primers or amplification parameters.
- The quality of the sample has a certain influence on the specificity. Therefore, high quality samples should be used for HRM analysis.
to sum up
HRM has high sensitivity and good specificity
The method is carried out in a closed test tube to reduce pollution. Therefore, the technique has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, less time, small error, and high-throughput detection. It is the preferred method for performing mutation scanning.
Lacto Helveticus,Lactobacillus Helveticus,Lactobacillus Helveticus Powder,Lactobacillus Helveticus Probiotic
Jiangsu Biodep Biotechnology Co. ,Ltd. , https://www.mbioda.com